Mutual TLS Server
Beeceptor's mock server supports Mutual TLS (mTLS) to mandate secure, authenticated connections between clients and your server endpoints. This feature allows you to issue authorized client certificates and enforce their presentation during the TLS handshake, ensuring that only verified clients can access your endpoint.
The mTLS feature is available for endpoints on the Team plan and above. You can enable and configure this feature directly from the Beeceptor dashboard.
Key Features:
- Certificate Management: Beeceptor generates signed certificates for clients to use during the handshake.
- Flexible and Strict Modes: Supports both flexible and strict mTLS options for different levels of security.
- Seamless Integration: Backward compatibility ensures your endpoints work with or without mTLS enabled.
Configuring Mutual TLS on Beeceptor
To set up Mutual TLS (mTLS) for your endpoint, follow these steps:
-
Go to the Your Endpoints > Endpoint Settings page from the user menu.
-
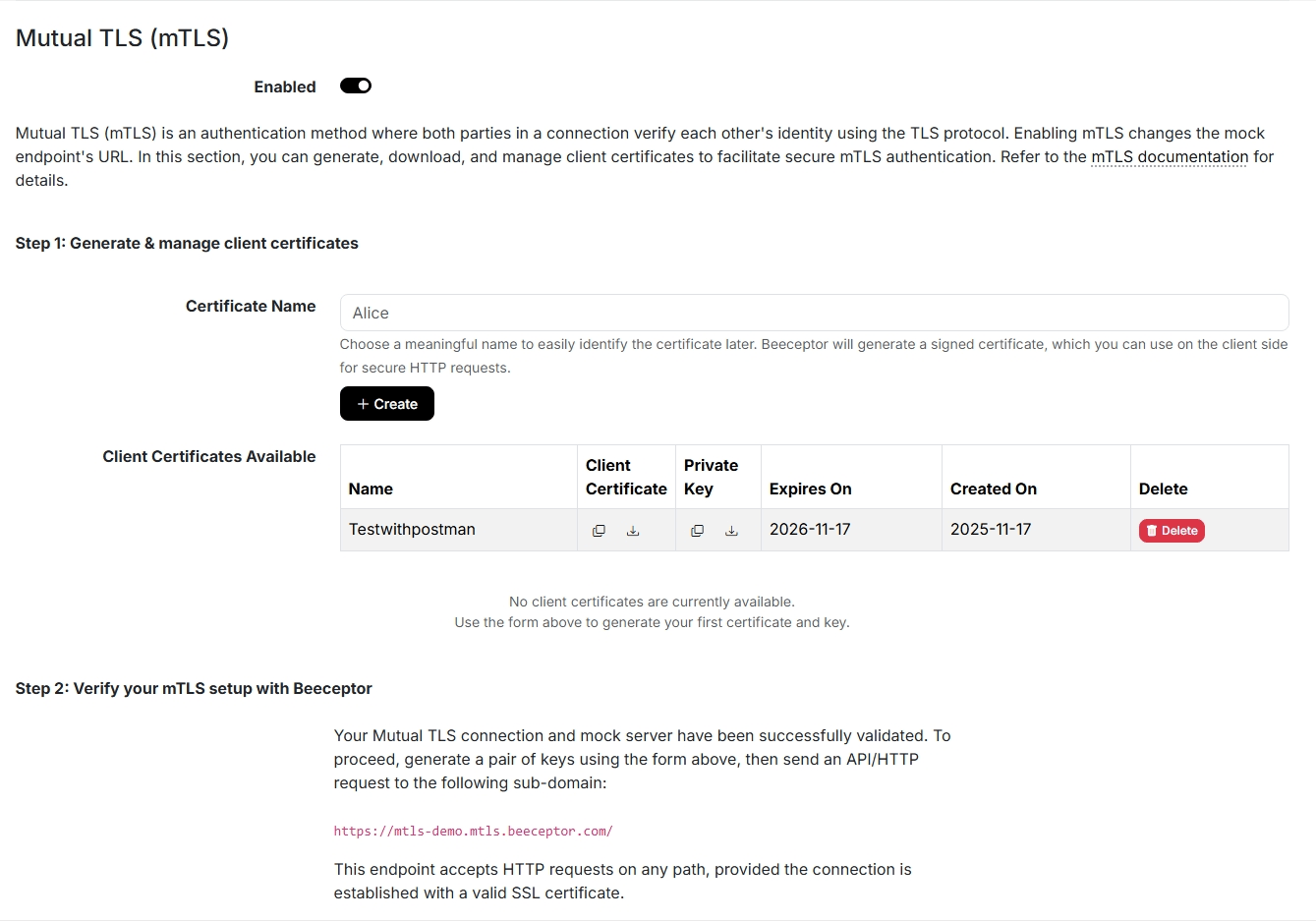
Scroll down to the Mutual TLS section and enable it.
-
After enabling mTLS, provide a name for key generation.
-
Beeceptor will automatically generate the required credentials, which include:
- Signed certificate (PEM format)
- Private key (PEM format)
Certificates created here are valid for one year.
Technical Specifications
Beeceptor has a built-in Certificate Authority (CA) for mTLS, so you don’t need to upload your own root CA or generate a custom chain.
Just enable mTLS on your endpoint, download the client certificate and key that Beeceptor creates, and use them in your client. The certificate already includes the required chain issued by Beeceptor’s internal CA, so your client only needs to present the Beeceptor-generated cert and key during the TLS handshake.
Beeceptor acts as the Root Certificate Authority (CA) for all generated certificates.
- Key Strength: RSA 4096 bits
- Hashing Algorithm: SHA-256
- CA Validity: 10 years
- Client Certificate Validity: 1 year
Endpoint Selection
When you enable Mutual TLS on Beeceptor, the system creates additional subdomains for your mock server to accommodate different levels of security. These endpoints allow flexibility in how clients connect to the mock server, catering to both mTLS-enabled and standard TLS-based connections.
Below are the three types of endpoints available when mTLS is activated:
1. Standard SSL Access
The first type of endpoint supports standard TLS connections and is accessible at a subdomain like:
https://<your-endpoint>.proxy.beeceptor.com/
This endpoint does not enforce mTLS. It operates using standard SSL/TLS, which means that the client can connect without presenting a certificate. This option is ideal for cases where you want to allow open access to the endpoint or for backward compatibility with clients that do not support mTLS. While it provides basic encryption and server authentication, it does not verify the client’s identity.
2. Flexible Mutual TLS
The second endpoint offers flexibility, supporting connections with or without mutual TLS. It is available at:
https://<your-endpoint>.mtls.beeceptor.com/
This endpoint is designed for scenarios where you need to gradually introduce mTLS into your workflow. Here's how it behaves:
- If the client provides a valid certificate signed by Beeceptor, the server validates the certificate, and the connection is established securely using mTLS.
- If an invalid or unsigned certificate is provided, the connection is rejected.
- If no certificate is presented, the server defaults to a standard TLS connection.
This mode is useful for transitioning systems where some clients are ready for mTLS while others are not.
3. Strict Mutual TLS
The strict mTLS endpoint enforces mandatory client authentication and ensures that only authorized clients with valid Beeceptor-signed certificates can connect. It is accessible via:
https://<your-endpoint>.rmtls.beeceptor.com/
With strict mTLS, every connection attempt is validated. If the client does not present a certificate, or if the certificate is invalid or unsigned by Beeceptor, the connection is immediately rejected. This endpoint is designed for high-security scenarios where you need to guarantee that only trusted and authenticated clients can access your service.
Strict mTLS is particularly suited for securing sensitive APIs, internal microservices communication, or integrations with third-party systems that require stringent security measures.
Testing with Client Certificates
You can verify your mTLS setup using command-line tools like curl. Ensure you have downloaded the generated certificate and private key.
# Syntax: curl -v --cert <cert_file> --key <key_file> <url>
curl -v \
--cert client-cert.pem \
--key client-key.pem \
https://<your-endpoint>.rmtls.beeceptor.com/
If the handshake is successful, you will see the server response. If the certificate is invalid or missing (for strict mode), the connection will fail during the SSL handshake.