Generate Fake Data For Mock API Response
Imagine that you want to prototype an app with realistic-looking data, but the backend APIs are not there yet. That's where Beeceptor comes in. With Beeceptor, you have access to a powerful template engine that uses Handlebars' syntax. You can easily generate fake data that looks and feels realistic, without the hassle of dealing with messy code.
Fake data helpers
Beeceptor uses popular Faker's comparable syntax. It becomes a breeze to generate small/large data using a mocked response template. You can use pretty much all the attributes from Faker namespaces.
Enabling faker template
By default, template engine is off. You need to explicitly mark a rule to enable usage of Handlebars template to generate fake data.
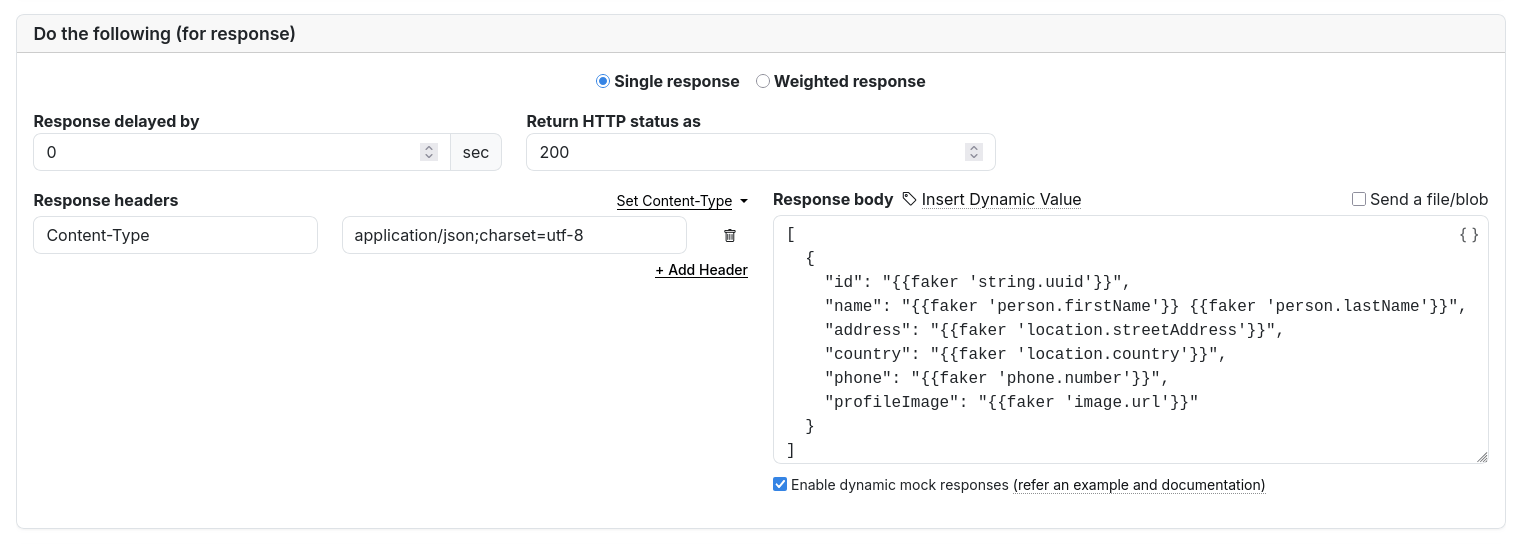
The faker Syntax
Beeceptor defines faker as a Handlebars template helper.
Faker attributes are grouped into namespaces. E.g. datatype, address, company, etc. To generate faked value for given attribute, prefix the attribute with its namespace. Refer below examples and values generated.
Syntax: {{faker 'namespace.attribute'}}
| Sample Syntax | Generated value |
|---|---|
{{faker 'string.uuid'}} | 52375efe-cf9e-44f5-adb2-65c1631bfcea |
{{faker 'location.country'}} | Spain |
{{faker 'finance.currencyCode'}} | USD |
{{faker 'hacker.phrase'}} | The AI hard drive is down, index the 1080p panel so we can override the COM firewall! |
{{faker 'lorem.paragraph'}} | Omnis perspiciatis provident error. Est possimus voluptates. Illo nam et excepturi blanditiis quae rerum et amet accusantium. Mollitia temporibus temporibus ea fugiat quia in possimus et. Ut provident est debitis perspiciatis ipsa non mollitia magnam quis. Et quod dolorum et non |
You can use the context menu in the template editor to insert dynamic expressions for test data generation. Start typing {{ followed by a keyword, and the menu will show a list of matching options. Selecting an item will insert the full syntax in place, which you can edit as needed.
Refer the section below to view complete list of supported attributes.
Example using mocking template
You can mix and match any of the Faker attributes to build a rich response. Consider the following example for GET /users API or model.
Mocking Template: A mocking template to build user objects.
[
{
"id" : "{{faker 'string.uuid'}}",
"name": "{{faker 'person.firstName'}} {{faker 'person.lastName'}}" ,
"address": "{{faker 'location.streetAddress'}}",
"country": "{{faker 'location.country'}}",
"phone": "{{faker 'phone.number'}}",
"profileImage": "{{faker 'image.url'}}",
},
{
"id" : "{{faker 'string.uuid'}}",
"name": "{{faker 'person.firstName'}} {{faker 'person.lastName'}}" ,
"address": "{{faker 'location.streetAddress'}}",
"country": "{{faker 'location.country'}}",
"phone": "{{faker 'phone.number'}}",
"profileImage": "{{faker 'image.url'}}",
}
]
Response: This will generate below output:
[
{
"id" : "cbe55c5d-36fa-4f05-9557-fcd4966187f4",
"name": "Dillon Davis" ,
"address": "613 Dickinson Run",
"country": "Tanzania",
"phone": "886.292.3509 x0831",
"profileImage": "http://placeimg.com/640/480/business",
},
{
"id" : "36df51a8-8d4c-4d70-8818-d77b9f6bf215",
"name": "Dannie Hackett" ,
"address": "8449 Brenna Alley",
"country": "Central African Republic",
"phone": "(786) 895-4923",
"profileImage": "http://placeimg.com/640/480/business",
}
]
Datatype classes
Use the following common constructs to generate random datatype values, string, uuid, etc.
number.float
number.int
datatype.boolean
string.string
string.hexadecimal
string.uuid
Number
Generate various number formats:
number.bigInt
number.binary
number.float
number.hex
number.int
number.octal
Whole number examples
| Syntax | Sample output |
|---|---|
{{faker 'number.int' '100000'}} | Generates a random number less than 100,000. 34746 |
{{faker 'number.int' '{min:500, max:600}'}} | Generates a random number in the range of 500 to 600.523 |
{{faker 'number.bigInt'}} | Generates a large random number.686544021836087 |
Floating point examples
| Syntax | Sample Output |
|---|---|
{{faker 'number.float'}} | Returns a random floating-point number, by default between 0.0 and 1.0. 0.7571638825 |
{{faker 'number.float' '100'}} | Returns a random floating-point number up to 100. 10.17630657 |
{{faker 'number.float' '{fractionDigits:2}'}} | Returns a random number between 0 and 1 with two decimal places. 0.39 |
{{faker 'number.float' '{min: 100, max: 1000, multipleOf:0.25}'}} | Returns a random number between 100 and 1000, multiple of 0.25. 516.75 |
String
Generate various string formats:
string.alpha
string.alphanumeric
string.binary
string.fromCharacters
string.hexadecimal
string.nanoid
string.numeric
string.octal
string.sample
string.symbol
string.uuid
Date
date.past
date.future
date.between
date.recent
date.month
date.weekday
Date Formatting - Syntax and Examples
When working with mock APIs, you might need to generate date values in a particular format. Beeceptor supports a range of date formatting options, enabling you to customize both standard and non-standard date outputs to suit your requirements.
You can generate date values using the following syntax with for a variety of formats. Below are some common examples:
| Use Case | Syntax Example | Output Example |
|---|---|---|
| Future Date in ISO Format | {{faker 'date.future' 'iso'}} | 2024-03-22T14:12:53.789+00:00 |
| Recent Date in UTC Format | {{faker 'date.recent' 'utc'}} | 2024-10-03T10:22:45Z |
| Future Timestamp in Milliseconds | {{faker 'date.future' 'timestamp'}} | 1734963456000 |
| Past Date in US Format | {{faker 'date.past' 'us'}} | 12/15/2021 |
| Custom Date Format (ISO with Milliseconds) | {{faker 'date.past' 'YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.SSSZ'}} | 2022-04-10T05:32:21.456+00:00 |
| Time Only in Custom Format | {{faker 'date.past' 'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ'}} | 11:45:32.123+00:00 |
| Past Date in European Format | {{faker 'date.past' 'eu'}} | 15/12/2021 |
| Full Human-readable Date Format | {{faker 'date.past' 'full'}} | Wednesday, April 10, 2022 5:32:21 AM |
| Compact Date Format for Unique ID | {{faker 'date.past' 'compact'}} | 20220410053221 |
| SQL Compatible Format | {{faker 'date.past' 'sql'}} | 2022-04-10 05:32:21 |
The examples above illustrate how to specify different formats using the faker function to meet your specific requirements.
Shorthand Date Formatting Options
Beeceptor supports several shorthand notations for date formatting. The table below shows these standard notations and their corresponding formats:
| Shorthand | Format Specification | Description |
|---|---|---|
iso | YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.SSSZ | ISO 8601 format with milliseconds; useful for international standards. |
iso8601 | YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.SSSZ | Another alias for ISO 8601, commonly used in APIs. |
rfc2822 | ddd, DD MMM YYYY HH:mm:ss ZZ | RFC 2822 format, often used for email headers. |
rfc3339 | YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ssZ | RFC 3339 format, suitable for machine-readable timestamps. |
w3c | YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ssZ | W3C standard for date and time on the web. |
unix | X | Unix epoch time in seconds, useful for Unix-based systems. |
timestamp | x | Unix epoch time in milliseconds; great for precise timestamps. |
short | YYYY-MM-DD | Short date format, ideal for compact displays of date only. |
long | YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss | Long format with time, typically used for detailed logs. |
full | dddd, MMMM D, YYYY h:mm:ss A | Full, human-readable date format; great for user interfaces. |
compact | YYYYMMDDHHmmss | Compact representation with no separators; useful for IDs. |
utc | YYYY-MM-DD[T]HH:mm:ss[Z] | UTC format, recommended for data that needs universal reference. |
sql | YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss | SQL-compatible format for database entries. |
us | MM/DD/YYYY | US date format, typically used in US-based applications. |
eu | DD/MM/YYYY | European date format, commonly used across Europe. |
Text classes
Lorem
Some blah blah... text and paragraphs.
lorem.word
lorem.words
lorem.sentence
lorem.slug
lorem.sentences
lorem.paragraph
lorem.paragraphs
lorem.text
lorem.lines
Word
Generate various word types:
word.adjective
word.adverb
word.conjunction
word.interjection
word.noun
word.preposition
word.pronoun
word.verb
word.words
Additional supported classes
Person Names
Generate first/last name, titles, job type, etc.
person.bio
person.firstName
person.fullName
person.gender
person.jobArea
person.jobDescriptor
person.jobTitle
person.jobType
person.lastName
person.middleName
person.prefix
person.sex
person.sexType
person.suffix
person.zodiacSign
Airline
Generate airline-related data:
airline.aircraftType
airline.airline
airline.airplane
airline.airport
airline.flightNumber
airline.recordLocator
airline.seat
Animal
Generate animal-related data:
animal.bear
animal.bird
animal.cat
animal.cetacean
animal.cow
animal.crocodilia
animal.dog
animal.fish
animal.horse
animal.insect
animal.lion
animal.rabbit
animal.rodent
animal.snake
animal.type
Location
Generate location-related data:
location.buildingNumber
location.cardinalDirection
location.city
location.country
location.countryCode
location.county
location.direction
location.latitude
location.longitude
location.nearbyGPSCoordinate
location.ordinalDirection
location.secondaryAddress
location.state
location.street
location.streetAddress
location.timeZone
location.zipCode
Phone Numbers
phone.imei
phone.number
E-commerce
Some realistic product names.
commerce.department
commerce.isbn
commerce.price
commerce.product
commerce.productAdjective
commerce.productDescription
commerce.productMaterial
commerce.productName
Company
company.name
company.catchPhrase
company.buzzPhrase
company.catchPhraseAdjective
company.catchPhraseDescriptor
company.catchPhraseNoun
company.buzzVerb
company.buzzNoun
company.buzzAdjective
Color
Generate color-related data:
color.cmyk
color.colorByCSSColorSpace
color.cssSupportedFunction
color.cssSupportedSpace
color.hsl
color.human
color.hwb
color.lab
color.lch
color.rgb
color.space
Finance
finance.accountNumber
finance.amount
finance.bic
finance.bitcoinAddress
finance.creditCardCVV
finance.creditCardIssuer
finance.creditCardNumber
finance.currency
finance.currencyCode
finance.currencyName
finance.currencySymbol
finance.ethereumAddress
finance.iban
finance.litecoinAddress
finance.pin
finance.routingNumber
finance.transactionDescription
finance.transactionType
Online Forum
hacker.abbreviation
hacker.adjective
hacker.noun
hacker.verb
hacker.ingverb
hacker.phrase
Images
Generates links to images for the following categories.
E.g.
The {{faker 'image.urlLoremFlickr' 'animals'}} syntax will generate a link to http://placeimg.com/640/480/animals. The image.url syntax will generate a link to any random image.
image.avatar
image.avatarGitHub
image.avatarLegacy
image.dataUri
image.url
image.urlLoremFlickr
image.urlPicsumPhotos
image.urlPlaceholder
Internet
internet.color
internet.displayName
internet.domainName
internet.domainSuffix
internet.email
internet.emoji
internet.httpMethod
internet.httpStatusCode
internet.ip
internet.ipv4
internet.ipv6
internet.mac
internet.password
internet.port
internet.protocol
internet.url
internet.userAgent
internet.userName
Database
database.column
database.type
database.collation
database.engine
Git
git.branch
git.commitDate
git.commitEntry
git.commitMessage
git.commitSha
Music
Generate music-related data:
music.genre
music.songName
System
system.commonFileExt
system.commonFileName
system.commonFileType
system.cron
system.directoryPath
system.fileExt
system.fileName
system.filePath
system.fileType
system.mimeType
system.networkInterface
system.semver
Science
Generate science-related data:
science.chemicalElement
science.unit
Vehicle
Generate vehicle-related data:
vehicle.bicycle
vehicle.color
vehicle.fuel
vehicle.manufacturer
vehicle.model
vehicle.type
vehicle.vehicle
vehicle.vin
vehicle.vrm
Troubleshooting
When there are syntax errors in defining templates, Beeceptor tries to recover safely and attempts to generate the mocked response. However, there can be unrecoverable errors.
- If the
fakersyntax has any issue, you shall getFaker Attribute Error: Missing or wrong syntaxin the response. - If there is an unrecoverable error, a response with
561HTTP status code is returned. In such cases, you should review the template's syntax and correct it.