gRPC Mock Server
Beeceptor’s gRPC Mock Server accepts a gRPC API definition, and gives you back a fully functional, AI-generated mock service. When you upload .proto file or a compiled protoset, Beeceptor automatically creates mock implementations for all defined RPC methods, including unary and streaming types. You can accelerate client development, testing, and integration workflows by removing the dependency on an early-stage or unavailable backend.
Introduction
What is gRPC?
gRPC is a high-performance, contract-first RPC framework built on Protocol Buffers. It offers strong typing, efficient binary payloads, support for various streaming modes, and automatic code generation for many programming languages.
Developers challenges
Despite these advantages, consumers of a gRPC service often face practical challenges early in development. Most client teams cannot proceed until the backend service is implemented, deployed, and reliably reachable. Even when a backend is available, shared environments may be unstable, incomplete, or constantly changing, which makes testing difficult. This creates bottlenecks for mobile, frontend, QA, and integration teams who need a predictable way to exercise RPC calls, experiment with message formats, or validate streaming behavior long before backend logic is finalized.
The Beeceptor addresses these challenges by producing a ready-to-use mock server directly from the service schema. This allows developers to test real RPC interactions, validate request/response formats, explore streaming behaviors, and simulate edge cases long before backend services are implemented.
Creating a mock server
Uploading and processing proto files
You can upload a single .proto file, or a compiled protoset from the endpoint's Settings page. Once uploaded, Beeceptor parses the schema, extracts service definitions, detects message structures, and generates test data to be used in request and response for RPC invocations.
Documentation and RPC exploration
After uploading your proto specification, navigate to the mock server page. Here, Beeceptor presents all detected gRPC operations with auto-generated sample request and response payloads. The platform fully supports advanced Protobuf constructs-including nested messages, enums, maps, oneof fields, and Google’s well-known types-ensuring accurate representation of your API surface.
To ensure robustness, Beeceptor implements recursion limits when generating example data, preventing infinite expansion in the case of deeply nested or cyclic message definitions.
For each RPC, Beeceptor automatically produces realistic examples of both incoming and outgoing messages. These examples are based on:
- The field types defined in the Protobuf schema
- Contextual test data generated with AI
- Supported message structures such as
mapsandone-offields
For instance, given a message:
message Profile {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
google.protobuf.Timestamp created_at = 3;
}
The default mocked response may include values like:
{
"name": "Alex Clark",
"age": 28,
"createdAt": "2024-05-18T10:23:00Z"
}
Supported RPC Types
Beeceptor fully supports all major gRPC communication patterns, allowing you to mock and test a wide range of service interactions:
- Unary RPCs: Traditional request-response mechanism where the client sends a single request and receives a single response. Typical use case: retrieving a user profile or a specific resource.
- Server-Streaming RPCs: The client initiates a single request, and the server returns a stream of multiple responses. Beeceptor enables you to configure the number of messages in the stream. Common scenario: real-time feeds or activity streams.
- Client-Streaming RPCs: The client streams a sequence of messages to the server, after which the server returns a single consolidated response. Example: uploading data in chunks and receiving an aggregate status or summary.
- Bidirectional Streaming RPCs: Both the client and the server can simultaneously send streams of messages on a shared connection. Beeceptor generates independent mock sequences for inbound and outbound streams to accurately simulate real-world bidirectional interactions.
This comprehensive support ensures that you can replicate and validate nearly any gRPC workflow, including complex streaming scenarios, without the need for a live backend.
JSON Deserialization
Beeceptor receives and serves gRPC payloads as standard Protobuf-encoded messages on the wire. However, the console and logging UI present those Protobuf messages as JSON so humans can read, inspect, and edit values easily. When you review these intercepted requests or generated responses on the dashboard, Beeceptor shows an equivalent JSON representation derived from the Protobuf schema. This is a debugging and editing convenience only.
Further, Beeceptor lets you author mock responses in JSON on the UI. When you save a JSON-based mock response, the system validates the JSON against the Protobuf schema and then serializes it to the correct Protobuf binary form before returning it over gRPC.
The JSON shown in the Beeceptor UI uses field names that closely match those in your .proto definition, typically preserving the original snake_case convention for clarity and consistency.
Server Reflection Support
The Beeceptor gRPC Mock Server provides server reflection enabled by default, allowing tools like grpcurl and Postman’s gRPC client to discover services and RPC methods without needing local proto files.
For example, the below grpcurl command shows all available services on this mock server. In the following grbde1691df590 is the Beeceptor endpoint name.
grpcurl grbde1691df590.free.beeceptor.com:443 list

Copy one of the service name, and aks the server for all RPC method names defined using the following command.
grpcurl grbde1691df590.free.beeceptor.com:443 list <service-name>
Disable server reflection: You have the option to disable server reflection if you prefer to restrict schema visibility or replicate production environments where reflection is not available. Disabling reflection affects only service discoverability through client tools; all gRPC methods and behaviors continue to function as usual.
Advanced Behavior Simulation
Simulate using mock rules
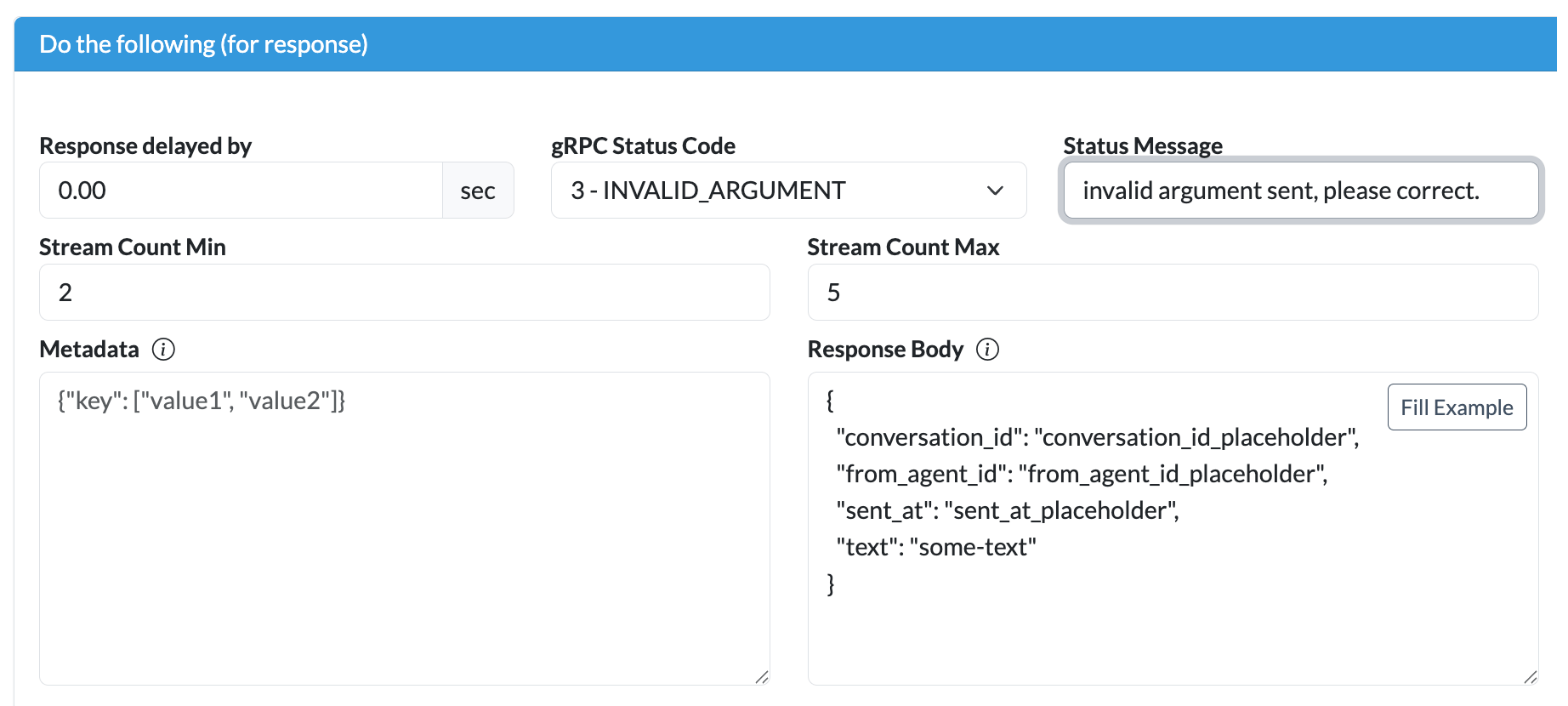
You can further customize mock responses by defining fixed outputs for your gRPC operations. Responses can be authored in JSON within the Beeceptor UI; these are automatically validated against the Protobuf schema and then converted into Protobuf-encoded messages for transmission to the client. This is similar to how HTTP mock rules work.
Beeceptor fully supports multiple server-side messages in both server-streaming and bidirectional-streaming RPCs. You can define the exact number of messages or specify a randomized range, and optionally inject delays to emulate real-world network latency.
gRPC Error Injection
Beeceptor also includes robust support for error simulation. You can configure precise gRPC error codes and custom messages on a per-request basis. These errors are sent following standard gRPC wire semantics, letting you thoroughly test client-side error handling and build resilient integrations.